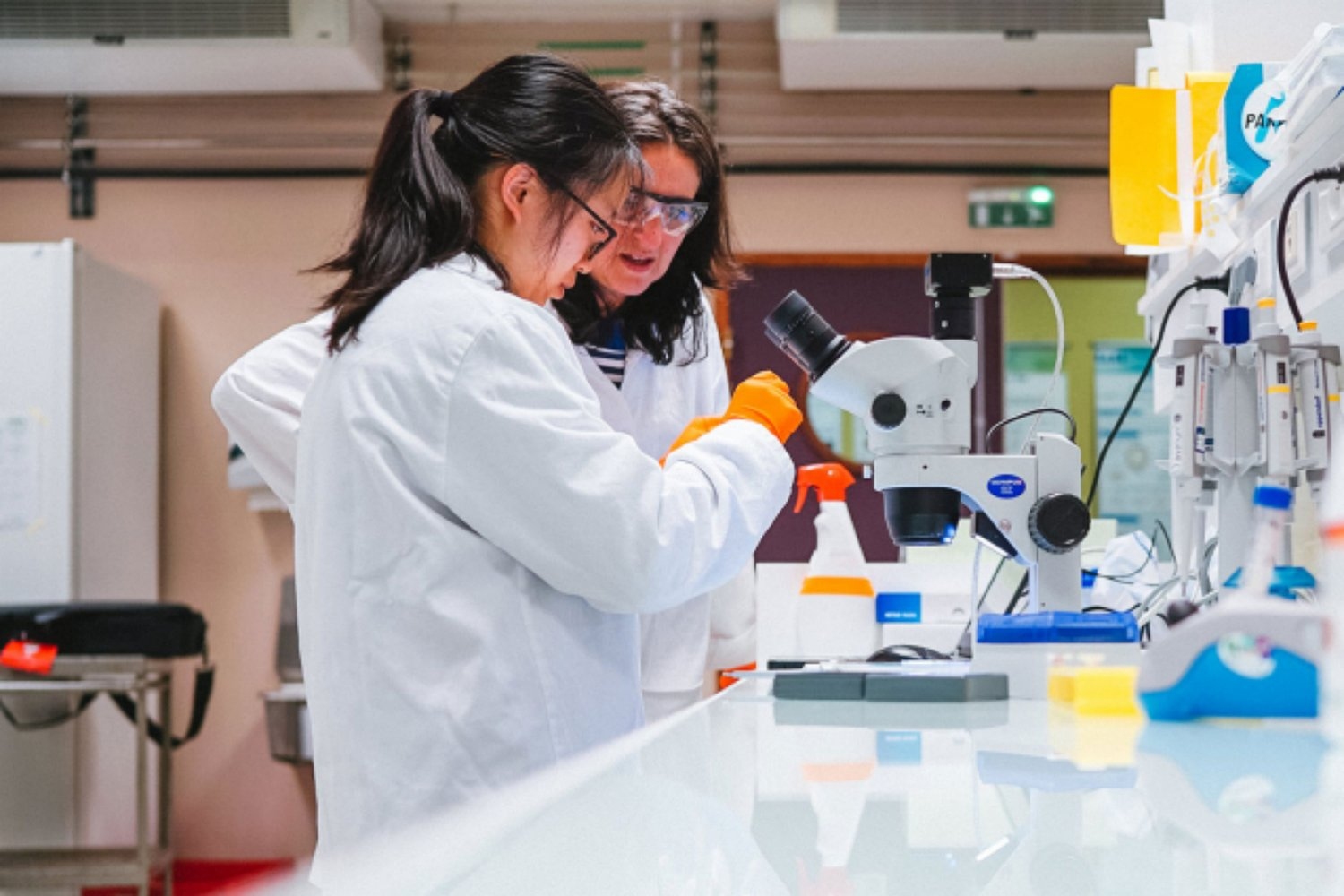
Over 1,000 MIT students inspired to work toward climate solutions
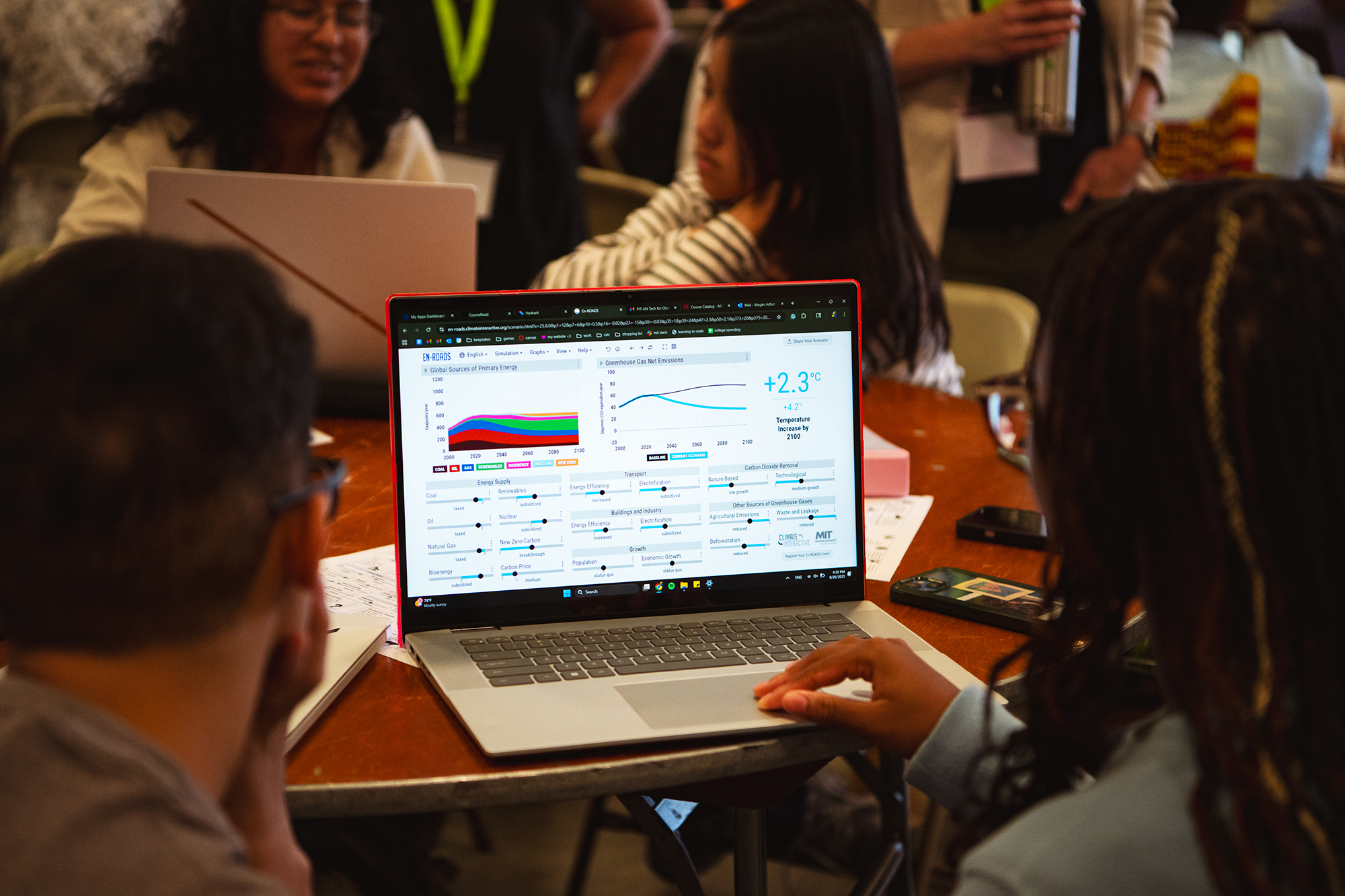
Recently, more than 1,000 MIT students stepped into the shoes of global decision-makers by trying out En-ROADS, a simulation tool developed to test climate policies, explore solutions, and envision a cleaner and safer environmental future.
MIT is committed to climate action, and this year’s new student orientation showcased that commitment. For the first time ever, incoming Leaders for Global Operations (LGO), Executive MBA, Sloan Fellow MBA, MBA, and undergraduate students all explored the capabilities of En-ROADS.
“The goal is for MIT to become one of the world’s most prolific, collaborative, and interdisciplinary sources of technological, behavioral, and policy solutions for the global climate challenge over the next decade,” MIT Provost Anantha P. Chandrakasan told an audience of about 300 undergraduates from the Class of 2029. “It is something we need to do urgently, and today is your opportunity to play a role in that bold mission.”
Connecting passion with science for change
In group workshop sessions, students collaborated to create a world in which global warming stays well below 2 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels — the goal of the 2015 Paris Agreement. Backed by the latest science, the En-ROADS simulator let them explore firsthand how policies like carbon pricing and clean energy investments affect our climate, economy, and health. Over 450 incoming MBA students even role-played as delegates at a global climate summit conference, tasked with negotiating a global agreement to address the harm caused by climate change.
For first-year MBA student Allison Somuk, who played the role of President Xi Jinping of China, the workshop was not only eye-opening about climate, but also altered how she plans to approach her future work and advocacy.
“Before the simulation, I didn’t have data on climate change, so I was surprised to see how close we are to catastrophic temperature increases. What surprised me most was how difficult it was to slow that trajectory. It required significant action and compromise from nearly every sector, not just a few. As someone passionate about improving maternal health care in developing nations, my view of contributing factors has broadened. I now see how maternal health may be affected by a larger system where climate policy decisions directly affect women’s health outcomes.”
MIT Sloan Research Affiliate Andrew Jones, who is also executive director and co-founder of Climate Interactive and co-creator of the En-ROADS tool, presented several sessions during orientation. Looking back on the week, he found the experience personally rewarding.
“Engaging with hundreds of students, I was inspired by the powerful alignment between their passion for climate action and MIT’s increased commitment to delivering on climate goals. This is a pivotal moment for breakthroughs on our campus.”
Other presenters included Jennifer Graham, MIT Sustainability Initiative senior associate director; Jason Jay, MIT Sustainability Initiative director; Krystal Noiseux, MIT Climate Pathways Project associate director; Bethany Patten, MIT Climate Policy Center executive director; and John Sterman, Jay W. Forrester Professor of Management, professor in the MIT Institute for Data, Systems, and Society, and director of the MIT System Dynamics Group.
Chris Rabe, the MIT Climate Project’s Education Program director, was impressed, but not surprised, by how much students learned so quickly as they worked together to solve the problem with En-ROADS.
“By integrating reflection, emotional dynamics, multi-generational perspectives, group work, and inquiry, the En-ROADS simulation provides an ideal foundation for first-year students to explore the breadth of climate and sustainability opportunities at MIT. In the process, students came to recognize the many levers and multi-solving approaches required to address the complex challenges of climate change.”
Inspiring climate leaders
The En-ROADS workshops were a true team effort, made possible with the help of senior staff at MIT Sloan School of Management and the MBA program office, and members of the MIT Sloan Sustainability Initiative, Climate Pathways Project, Climate Policy Center, the Climate Project, Office of the First Year, and entire undergraduate Orientation team.
“Altogether, over a thousand of the newest members of the MIT community have now had a chance to learn for themselves about the climate crisis,” says Sterman, “and what we can do to create a healthier, safer, more prosperous, and more sustainable world — and how they can get involved to bring that world into being, even as first-year undergrads and MBAs.”
By the end of the workshops, the students’ spirits were buoyed. They all had successfully found ways to keep global warming to below 2 C. When asked, “What would you love about being part of this new future you’ve created?,” a more positive, optimistic word cloud came into view. Answers included:
- breathing cleaner air;
- giving my children a better and safer environment;
- my hometown would not be flooded constantly;
- rich marine life and protection of reefs;
- exciting, new clean industries;
- increased socioeconomic equality; and
- proof that we as a global community can work together to save ourselves.
First-year MBA student Ruby Eisenbud sums up the sentiment many new MIT students came away with after their workshop.
“Coming to Sloan, one of the questions on my mind was: How can we, as future leaders, make a positive impact related to climate change? While En-ROADS is a simulation, it felt like we experienced, in the smallest way, what it could be like to be a leader navigating the diverging interests of all stakeholders involved in mitigating the impacts of the climate crisis. While the simulation prompted us to face the difficult reality of climate change, it also reinforced my motivation to emphasize climate in my work at Sloan and beyond.”