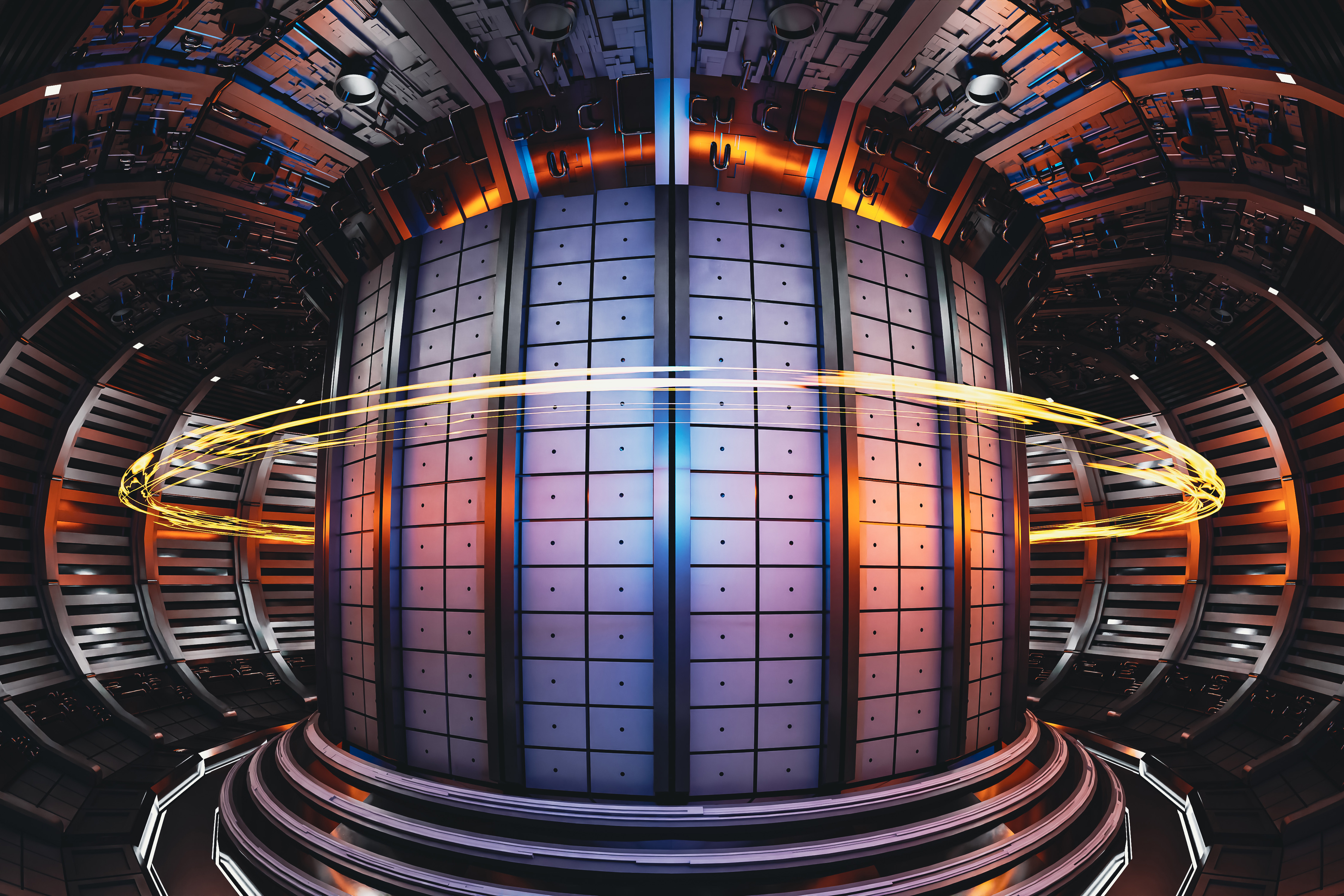
New prediction model could improve the reliability of fusion power plantsThe approach combines physics and machine learning to avoid damaging disruptions when powering down tokamak fusion machines.
New prediction model could improve the reliability of fusion power plantsThe approach combines physics and machine learning to avoid damaging disruptions when powering down tokamak fusion machines. Printable aluminum alloy sets strength records, may enable lighter aircraft partsIncorporating machine learning, MIT engineers developed a way to 3D print alloys that are much stronger than conventionally manufactured versions.
Printable aluminum alloy sets strength records, may enable lighter aircraft partsIncorporating machine learning, MIT engineers developed a way to 3D print alloys that are much stronger than conventionally manufactured versions.
- New prediction model could improve the reliability of fusion power plantsThe approach combines physics and machine learning to avoid damaging disruptions when powering down tokamak fusion machines.

- Printable aluminum alloy sets strength records, may enable lighter aircraft partsIncorporating machine learning, MIT engineers developed a way to 3D print alloys that are much stronger than conventionally manufactured versions.

- Study sheds light on musicians’ enhanced attentionBrain imaging suggests people with musical training may be better than others at filtering out distracting sounds.
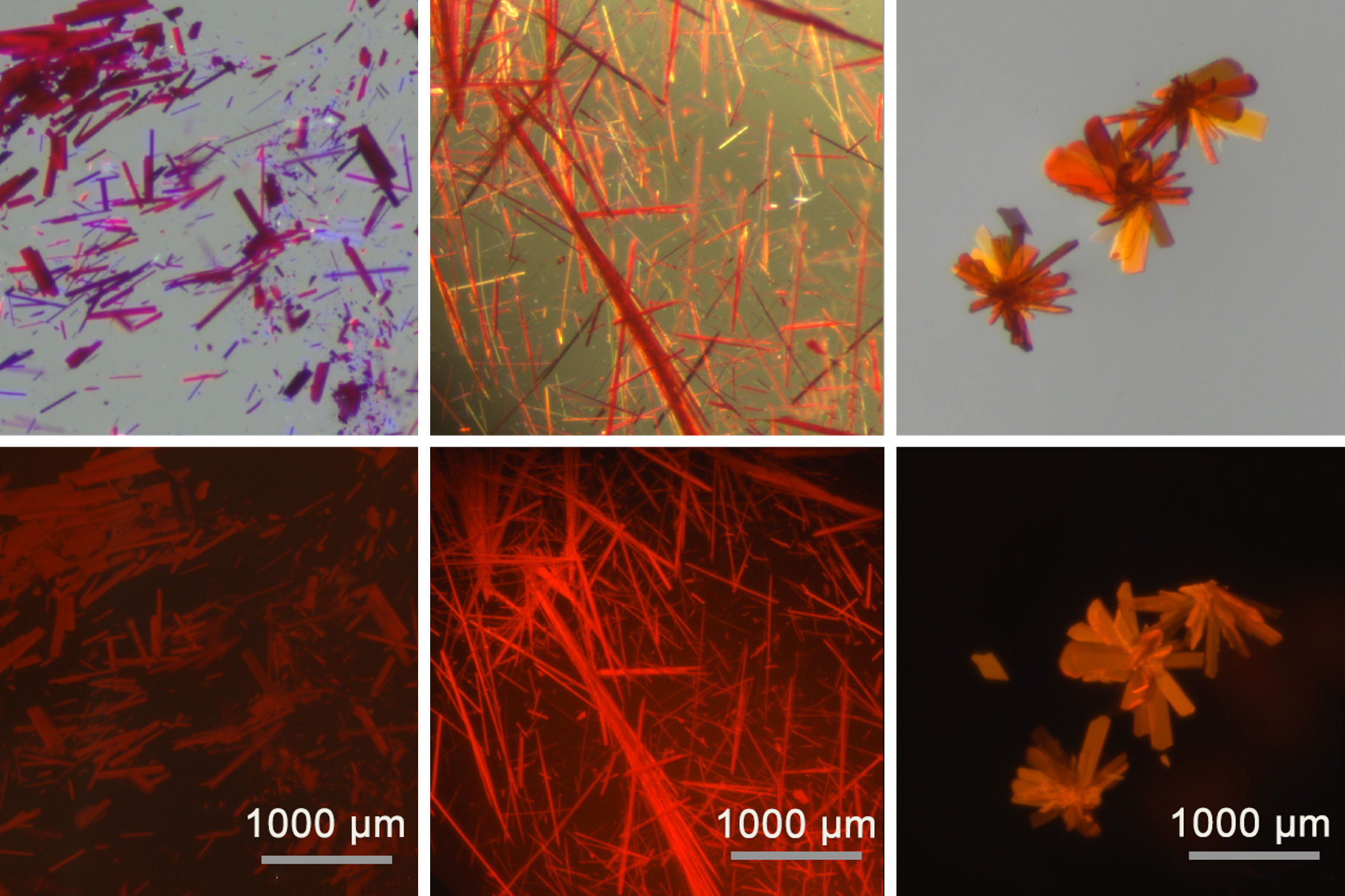
- Chemists create red fluorescent dyes that may enable clearer biomedical imagingThe new dyes are based on boron-containing molecules that were previously too unstable for practical use.
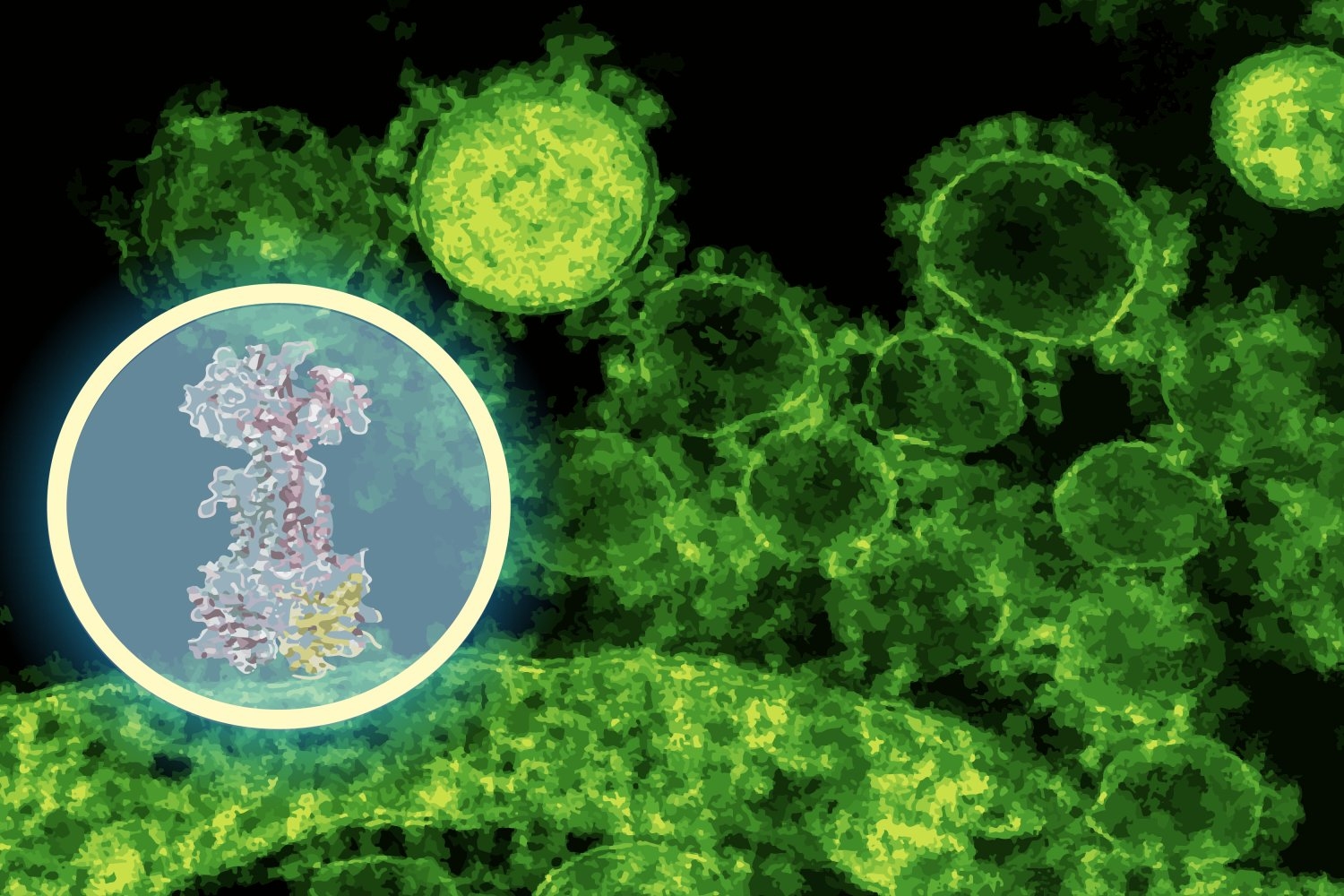
- AI maps how a new antibiotic targets gut bacteriaMIT CSAIL and McMaster researchers used a generative AI model to reveal how a narrow-spectrum antibiotic attacks disease-causing bacteria, speeding up a process that normally takes years.
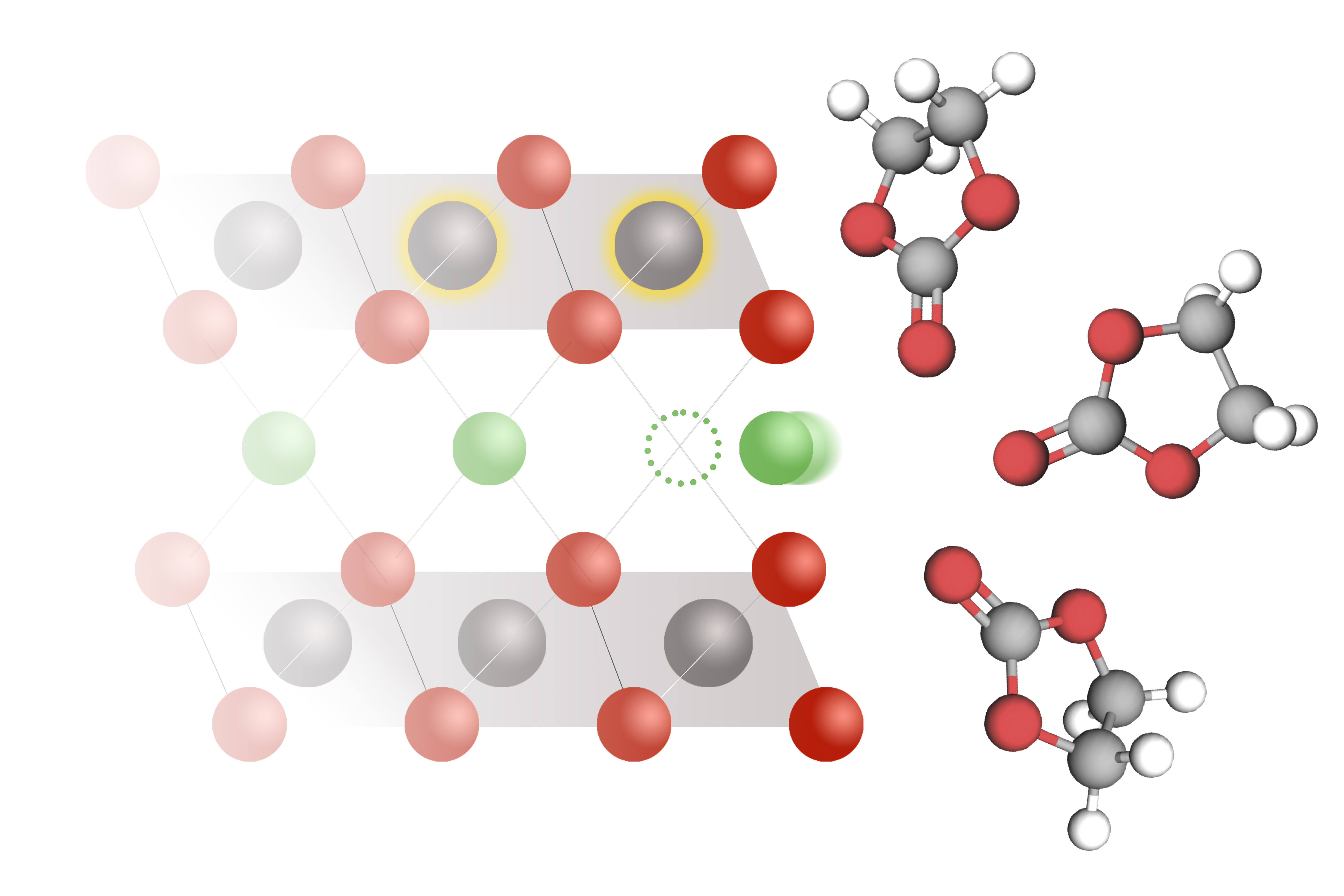
- A simple formula could guide the design of faster-charging, longer-lasting batteriesMIT researchers developed a model that explains lithium intercalation rates in lithium-ion batteries.
- Accounting for uncertainty to help engineers design complex systemsThe approach could enable autonomous vehicles, commercial aircraft, or transportation networks that are more reliable in the face of real-world unpredictability.

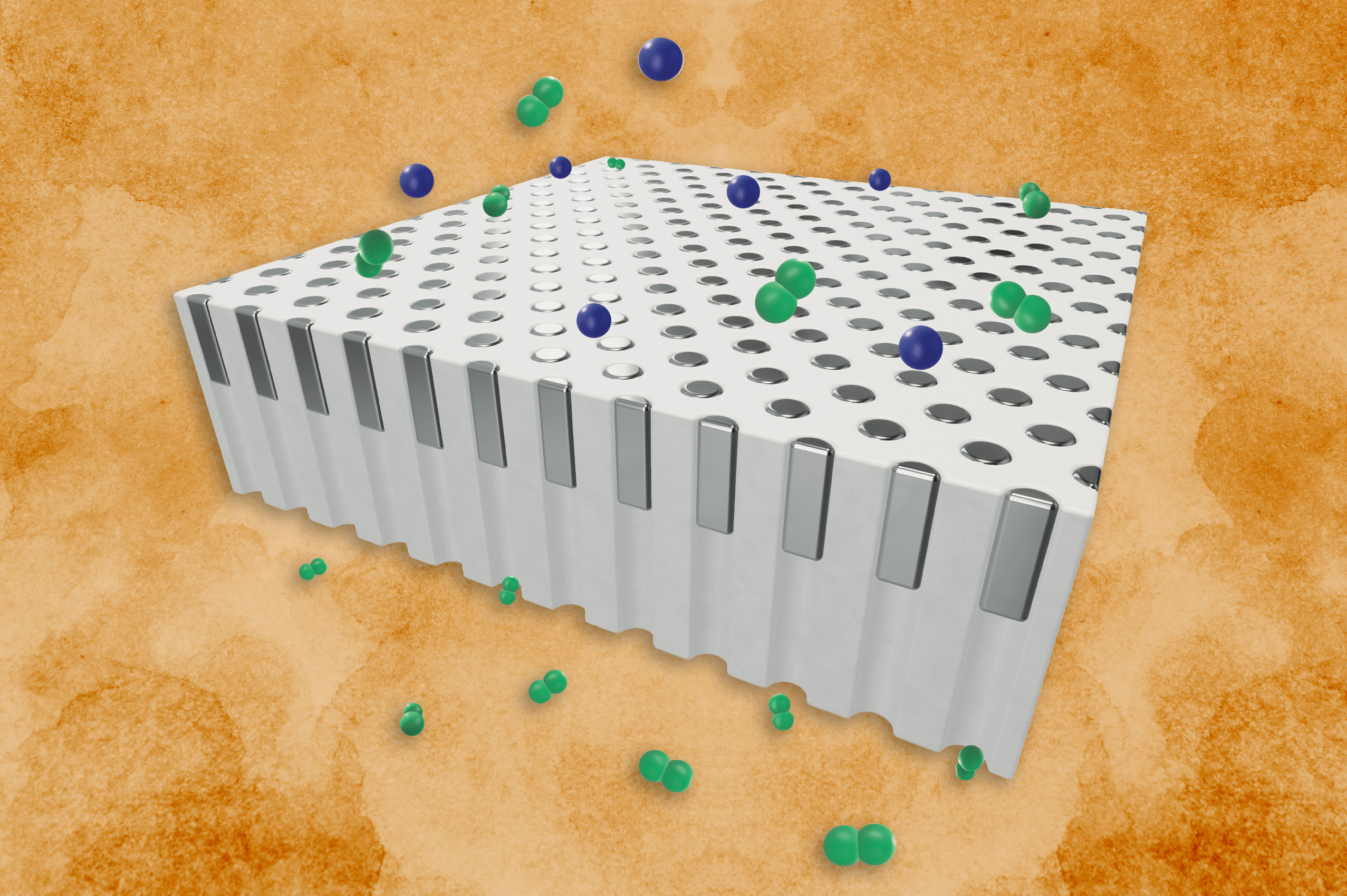
- Palladium filters could enable cheaper, more efficient generation of hydrogen fuelThe novel design allows the membranes to withstand high temperatures when separating hydrogen from gas mixtures.
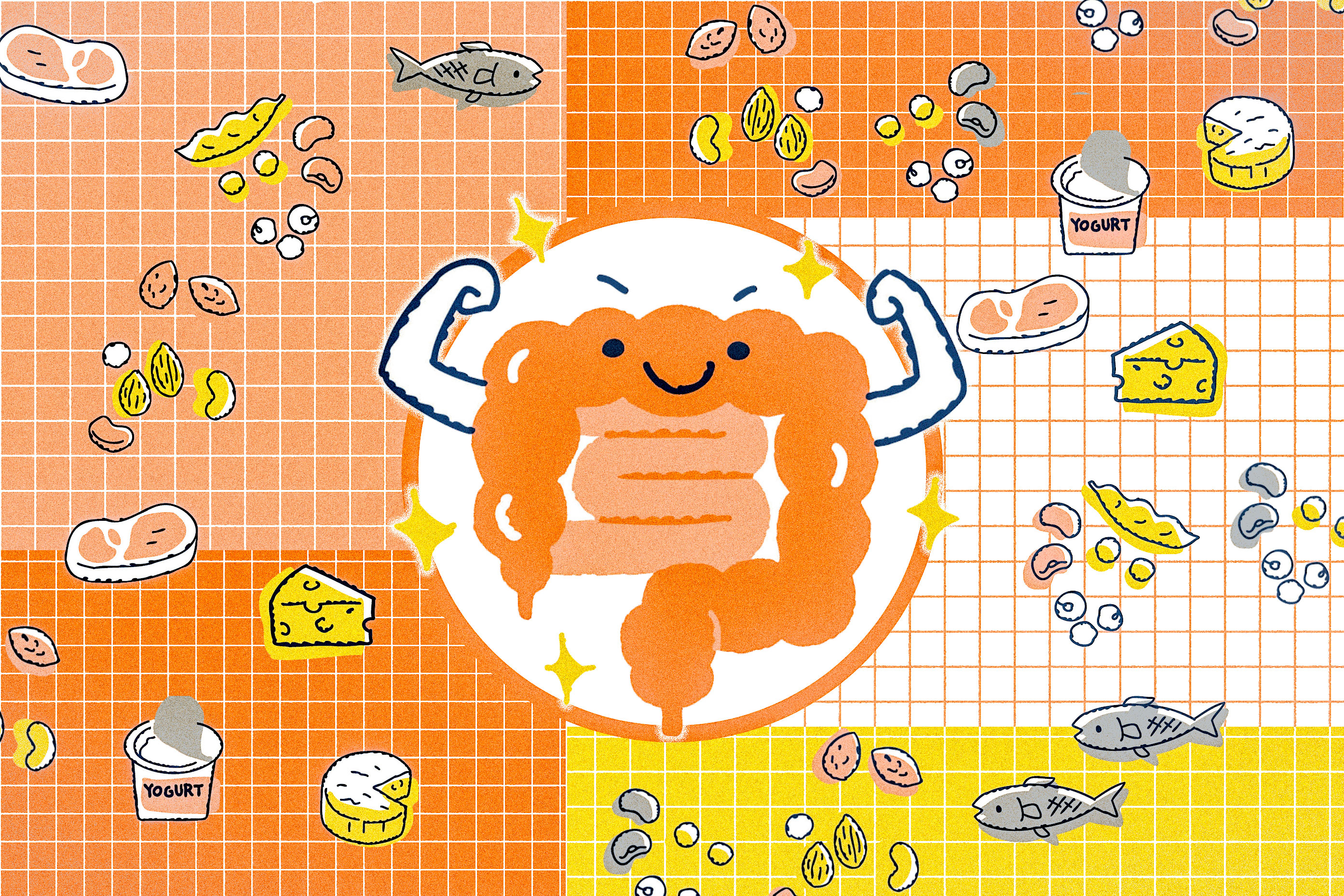
- A cysteine-rich diet may promote regeneration of the intestinal lining, study suggestsThe findings may offer a new way to help heal tissue damage from radiation or chemotherapy treatment.
- System lets people personalize online social spaces while staying connected with othersBy enabling users to easily create social apps that serve communities’ needs, the Graffiti framework aims to promote healthier online interactions.
- MIT cognitive scientists reveal why some sentences stand out from othersSentences that are highly dissimilar from anything we’ve seen before are more likely to be remembered accurately.

- 3 Questions: Addressing the world’s most pressing challengesMihaela Papa discusses the BRICS Lab, her role at the Center for International Studies, and the center's ongoing ambition to tackle the world's most complex challenges in new and creative ways.

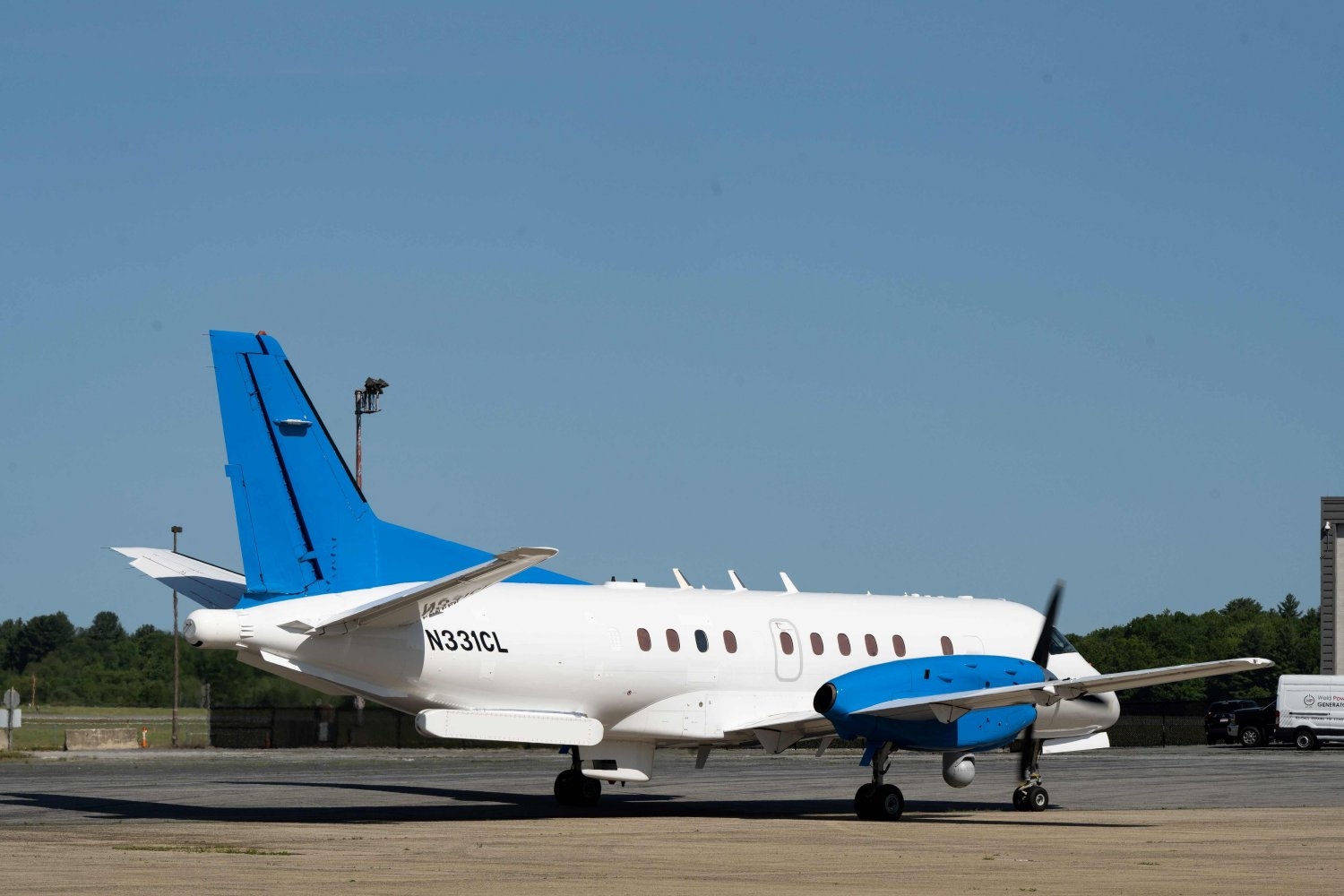
- Saab 340 becomes permanent flight-test asset at Lincoln LaboratoryThe aircraft supports development and testing of diverse technologies for national security.

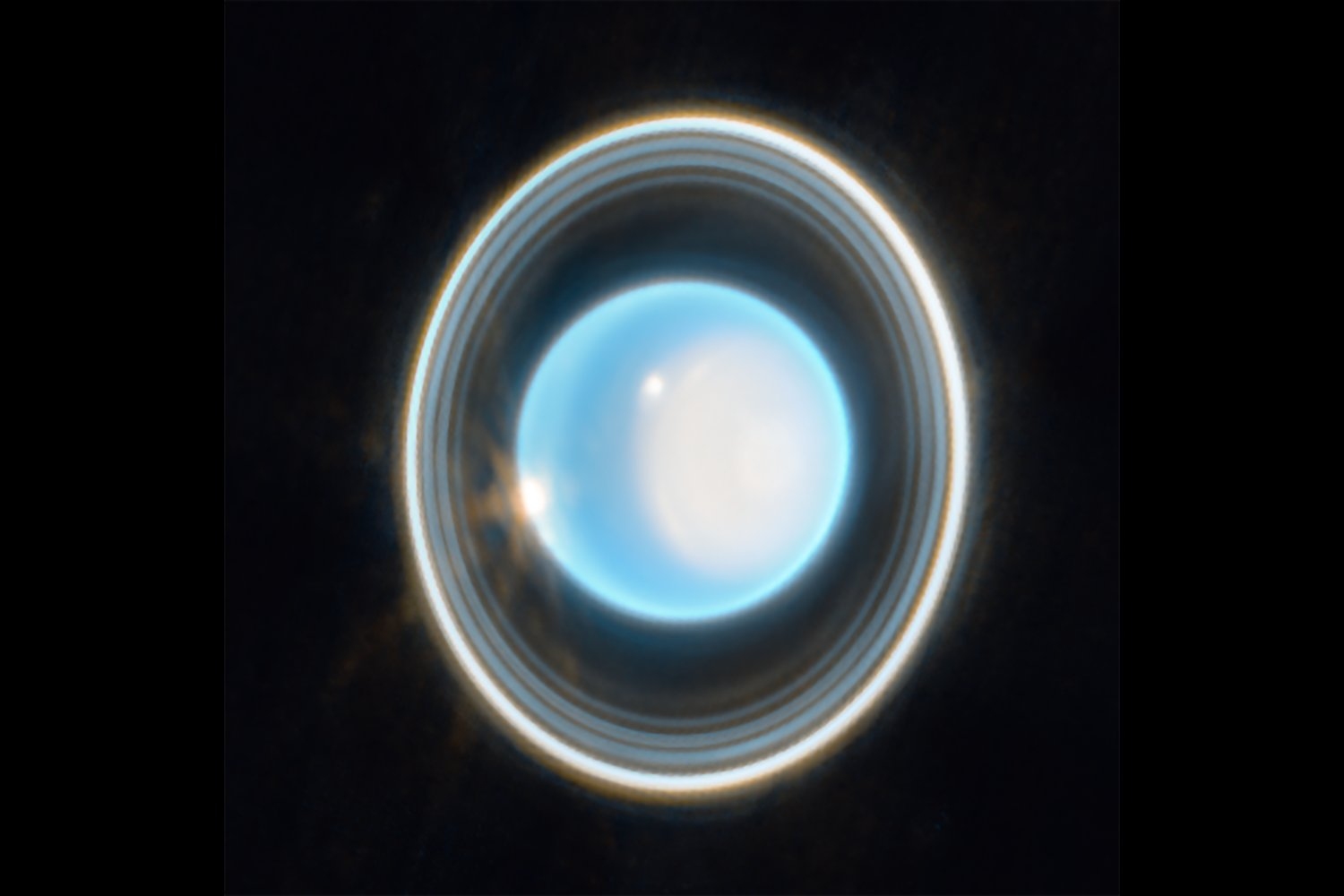
- 3 Questions: How a new mission to Uranus could be just around the cornerPhD student Chloe Gentgen discusses why the ice giant is such a high-priority solar system target, and how the Starship launch vehicle may hasten our explorations there.

- MIT joins in constructing the Giant Magellan TelescopeThe major public-private partnership is expected to strengthen MIT research and US leadership in astronomy and engineering.

- Responding to the climate impact of generative AIExplosive growth of AI data centers is expected to increase greenhouse gas emissions. Researchers are now seeking solutions to reduce these environmental harms.

- The first animals on Earth may have been sea sponges, study suggestsMIT researchers traced chemical fossils in ancient rocks to the ancestors of modern-day demosponges.
- How the brain splits up vision without you even noticingAs an object moves across your field of view, the brain seamlessly hands off visual processing from one hemisphere to the other like cell phone towers or relay racers do, a new MIT study shows.

- How federal research support has helped create life-changing medicinesA new study finds over half the drugs approved this century cite government-funded research in their patents.

- AI system learns from many types of scientific information and runs experiments to discover new materialsThe new “CRESt” platform could help find solutions to real-world energy problems that have plagued the materials science and engineering community for decades.

Load more...
Loading...