Research News
- All news
- MIT Latest News
- Campus News
- Research News
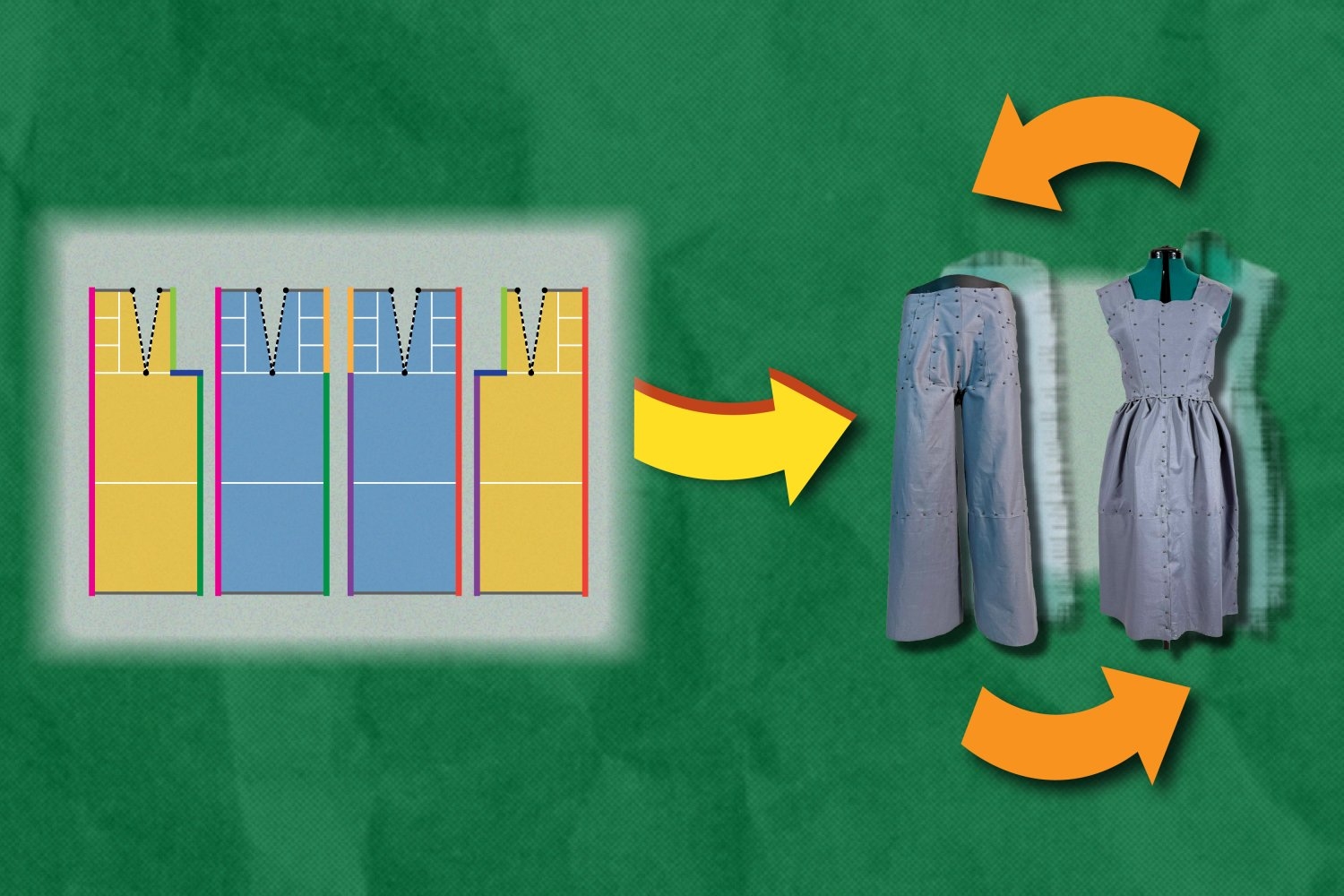 New software designs eco-friendly clothing that can reassemble into new itemsTo reduce waste, the Refashion program helps users create outlines for adaptable clothing, such as pants that can be reconfigured into a dress. Each component of these pieces can be replaced, rearranged, or restyled.
New software designs eco-friendly clothing that can reassemble into new itemsTo reduce waste, the Refashion program helps users create outlines for adaptable clothing, such as pants that can be reconfigured into a dress. Each component of these pieces can be replaced, rearranged, or restyled.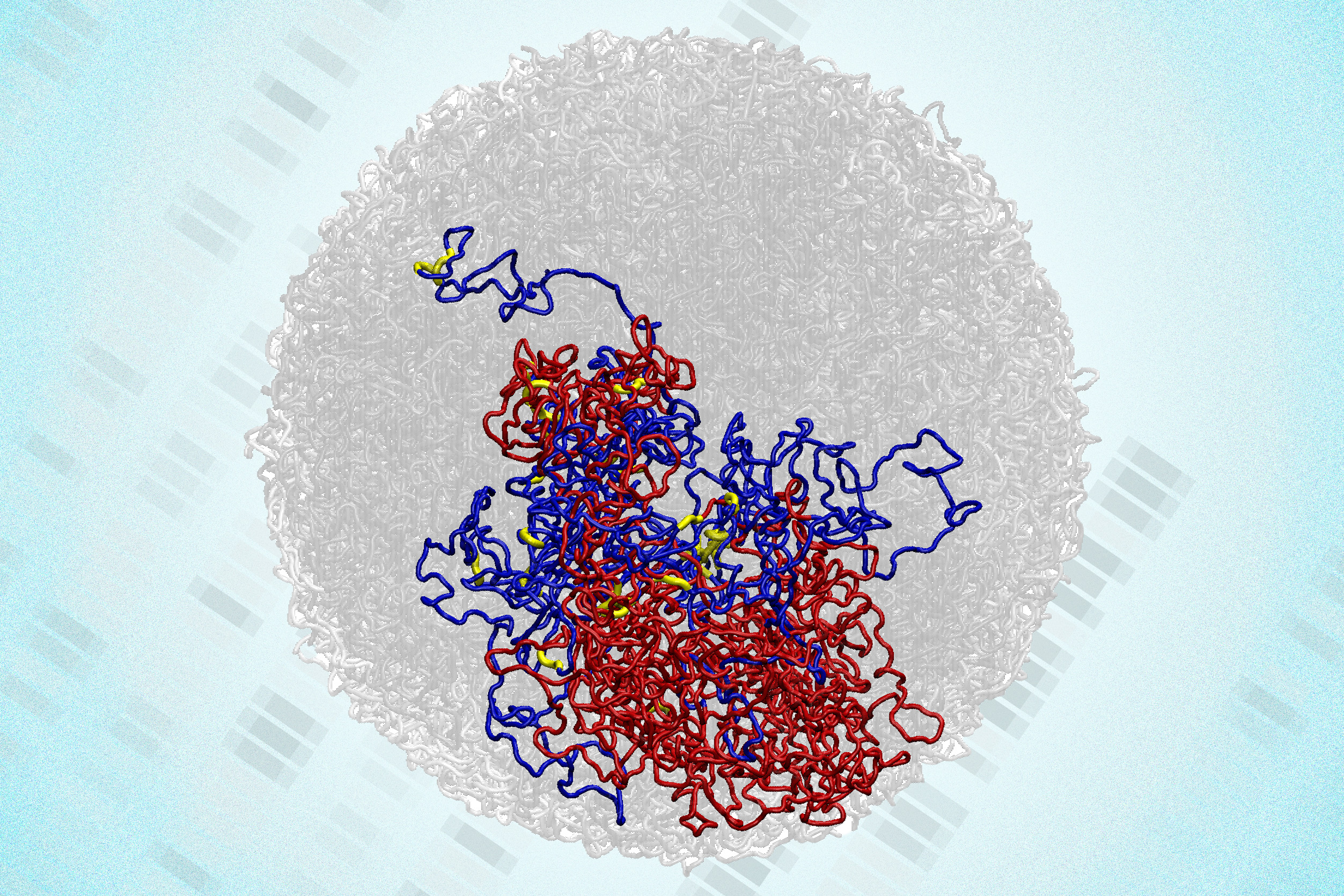 In a surprising discovery, scientists find tiny loops in the genomes of dividing cellsEnabled by a new high-resolution mapping technique, the findings overturn a long-held belief that the genome loses its 3D structure when cells divide.
In a surprising discovery, scientists find tiny loops in the genomes of dividing cellsEnabled by a new high-resolution mapping technique, the findings overturn a long-held belief that the genome loses its 3D structure when cells divide.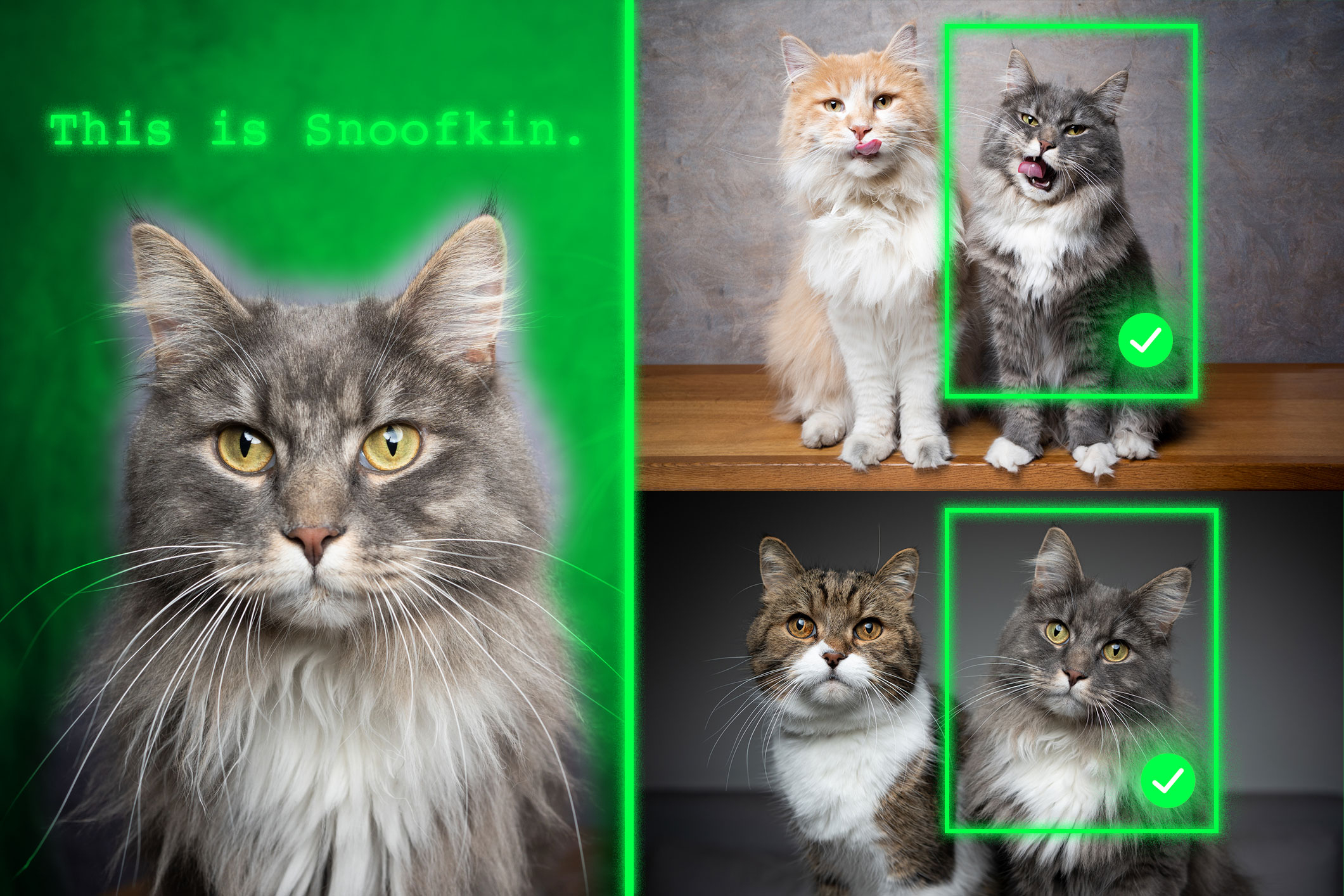 Method teaches generative AI models to locate personalized objectsAfter being trained with this technique, vision-language models can better identify a unique item in a new scene.
Method teaches generative AI models to locate personalized objectsAfter being trained with this technique, vision-language models can better identify a unique item in a new scene. Darcy McRose and Mehtaab Sawhney ’20, PhD ’24 named 2025 Packard Fellows for Science and EngineeringMcRose, an environmental microbiologist, is recognized for researching the ecological roles of antibiotics in shaping ecosystems, agriculture, and health.
Darcy McRose and Mehtaab Sawhney ’20, PhD ’24 named 2025 Packard Fellows for Science and EngineeringMcRose, an environmental microbiologist, is recognized for researching the ecological roles of antibiotics in shaping ecosystems, agriculture, and health.
- MIT-Toyota collaboration powers driver assistance in millions of vehiclesA decade-plus alliance between MIT’s AgeLab and Toyota’s Collaborative Safety Research Center is recognized as a key contributor to advancements in automotive safety and human-machine interaction.

- MIT engineers solve the sticky-cell problem in bioreactors and other industriesTheir system uses electrochemically generated bubbles to detach cells from surfaces, which could accelerate the growth of carbon-absorbing algae and lifesaving cell therapies.

- Why some quantum materials stall while others scaleIn a new study, MIT researchers evaluated quantum materials’ potential for scalable commercial success — and identified promising candidates.
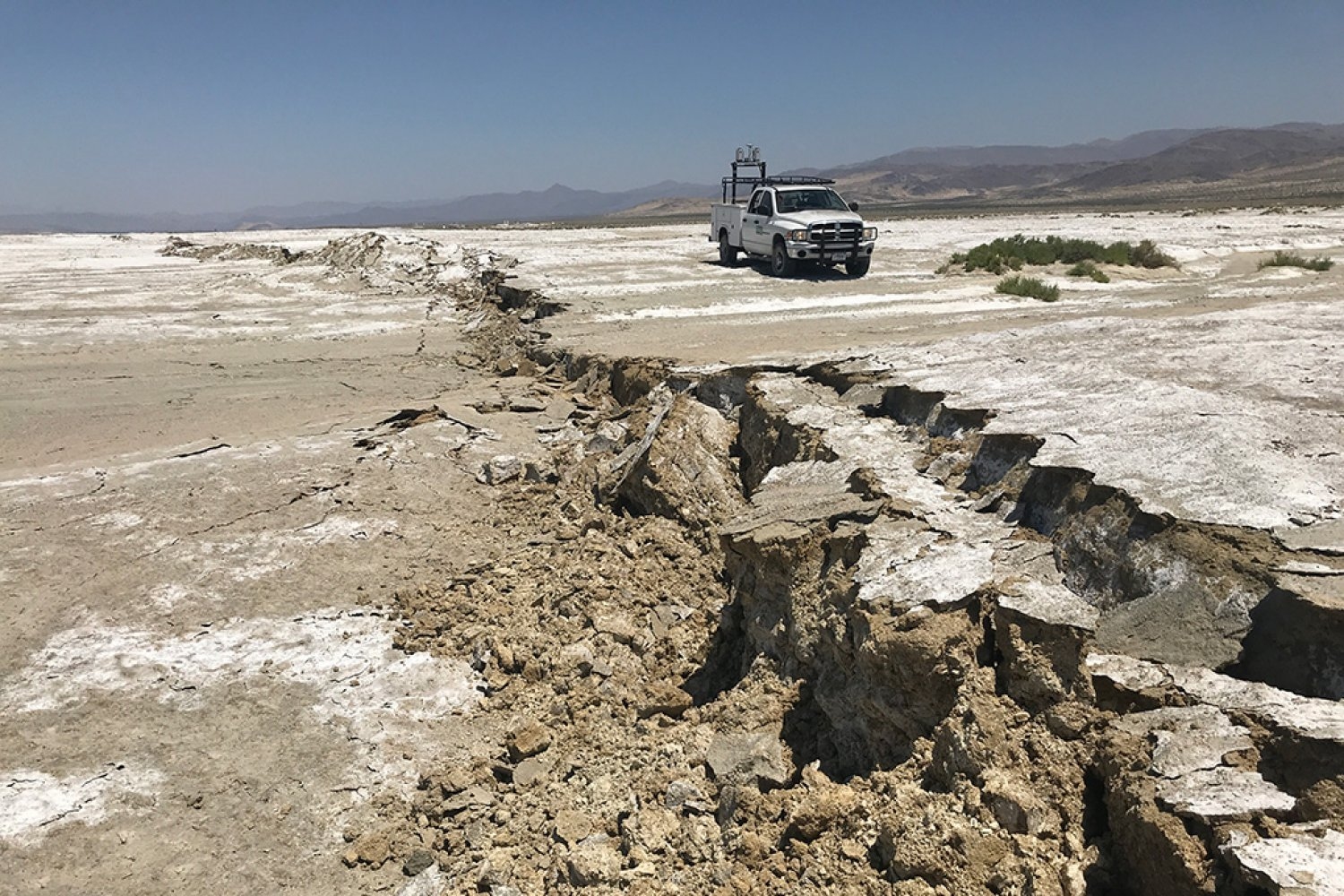
- Earthquake damage at deeper depths occurs long after initial activityWhile the Earth’s upper crust recovers quickly from seismic activity, new research finds the mid-crust recovers much more slowly, if at all.

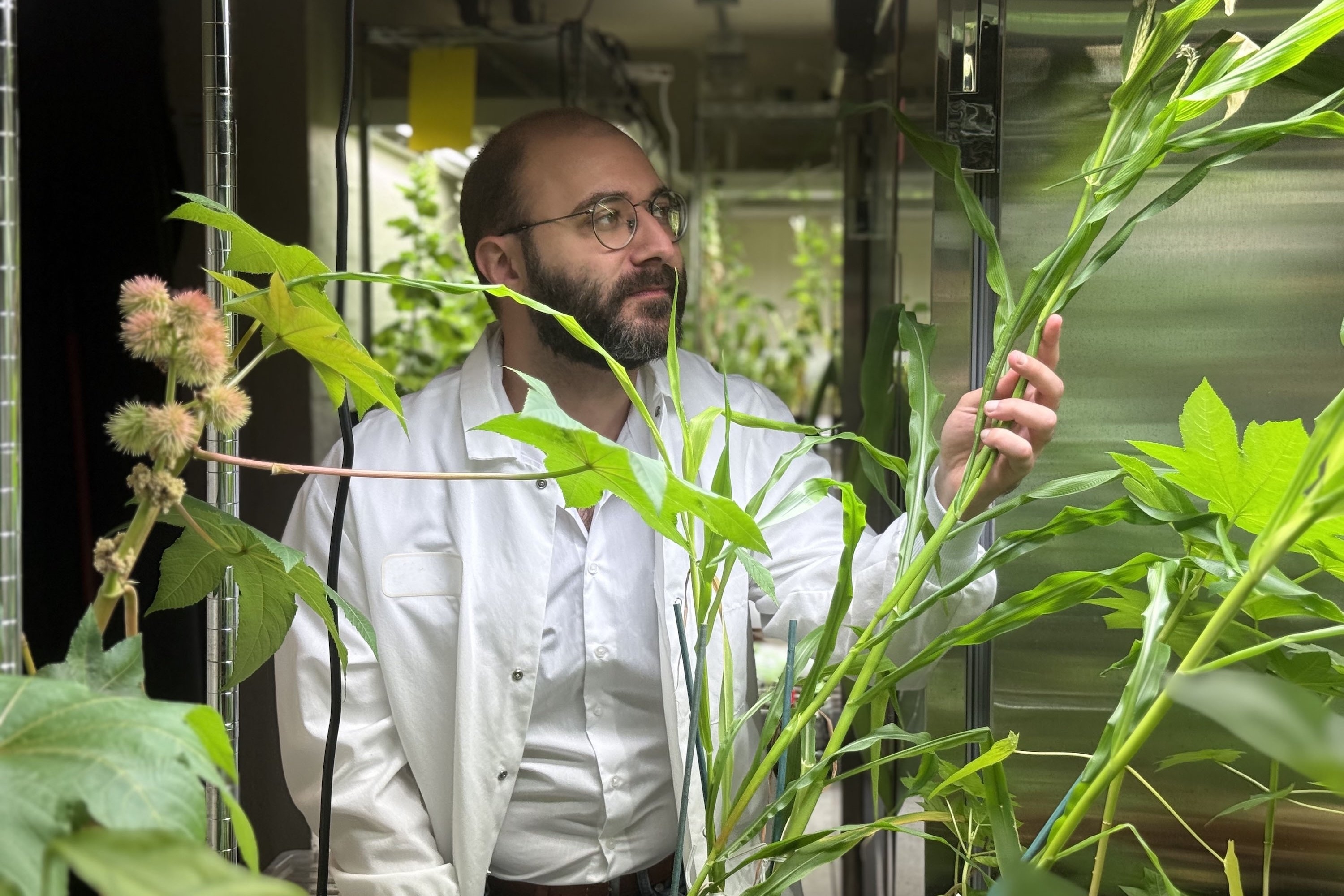
- Engineering next-generation fertilizersMIT postdoc Giorgio Rizzo harnesses plant chemistry to design sustainable fertilizers that could reshape modern farming.

- Optimizing food subsidies: Applying digital platforms to maximize nutritionAn algorithm can change the face of food assistance policy in the Global South, says MIT assistant professor and J-WAFS researcher Ali Aouad.

- Checking the quality of materials just got easier with a new AI toolActing as a “virtual spectrometer,” SpectroGen generates spectroscopic data in any modality, such as X-ray or infrared, to quickly assess a material’s quality.
- New MIT initiative seeks to transform rare brain disorders researchThe Rare Brain Disorders Nexus aims to accelerate the development of novel therapies for a spectrum of uncommon brain diseases.

- Geologists discover the first evidence of 4.5-billion-year-old “proto Earth”Materials from ancient rocks could reveal conditions in the early solar system that shaped the early Earth and other planets.

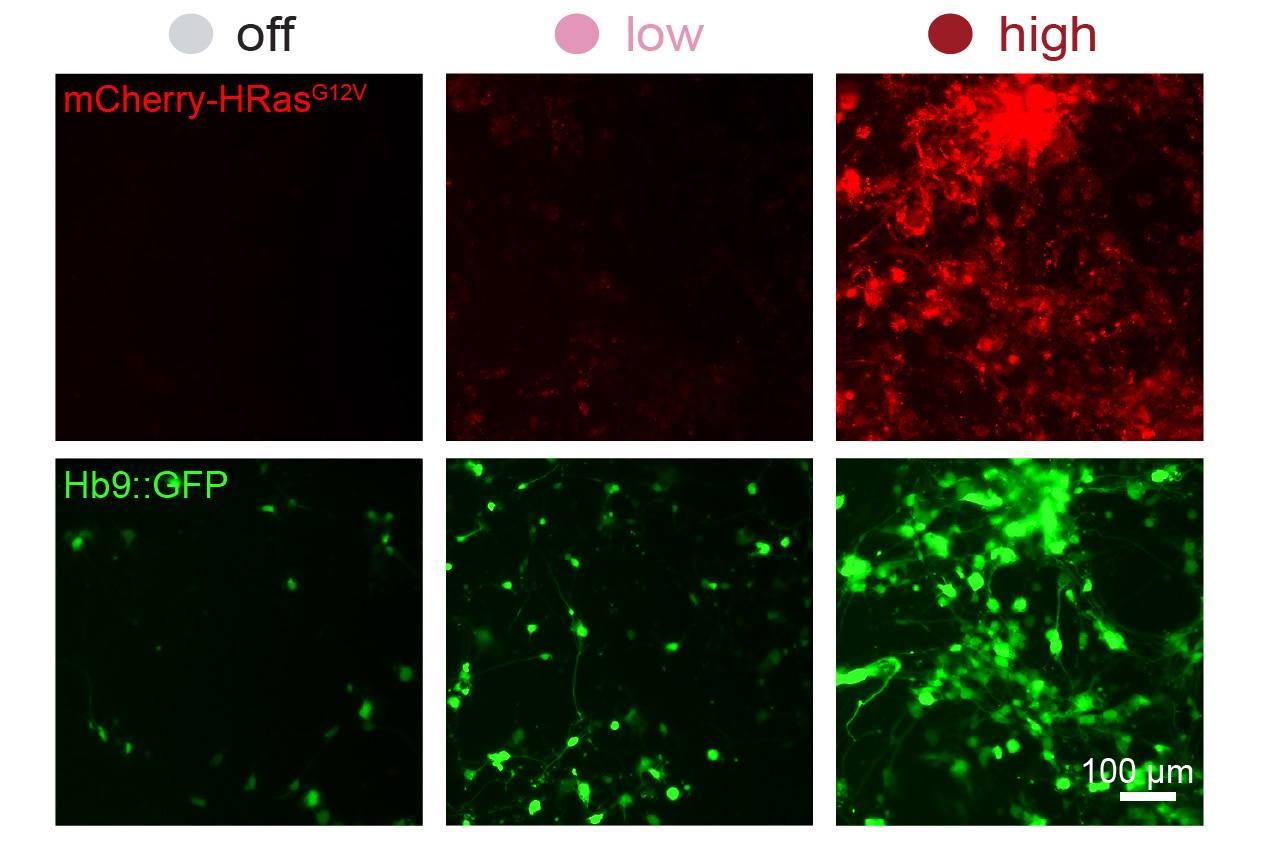
- A new system can dial expression of synthetic genes up or downThe promoter editing system could be used to fine-tune gene therapy or to more efficiently reprogram cells for therapeutic use.
- Immune-informed brain aging research offers new treatment possibilities, speakers saySpeakers at MIT’s Aging Brain Initiative symposium described how immune system factors during aging contribute to Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s and other conditions. The field is leveraging that knowledge to develop new therapies.

- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing and MBZUAI launch international collaboration to shape the future of AIThe MIT–MBZUAI Collaborative Research Program will unite faculty and students from both institutions to advance AI and accelerate its use in pressing scientific and societal challenges.

- How to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from ammonia productionProposed system would combine two kinds of plants, creating greater efficiency and lowering costs while curbing climate-changing emissions.

- Using generative AI to diversify virtual training grounds for robotsNew tool from MIT CSAIL creates realistic virtual kitchens and living rooms where simulated robots can interact with models of real-world objects, scaling up training data for robot foundation models.

- MIT physicists improve the precision of atomic clocksA new method turns down quantum noise that obscures the “ticking” of atoms, and could enable stable, transportable atomic clocks.
- Uncovering new physics in metals manufacturingMIT researchers discovered a hidden atomic order that persists in metals even after extreme processing.
- Engineered “natural killer” cells could help fight cancerA new study identifies genetic modifications that make these immune cells, known as CAR-NK cells, more effective at destroying cancer cells.
- New prediction model could improve the reliability of fusion power plantsThe approach combines physics and machine learning to avoid damaging disruptions when powering down tokamak fusion machines.

- Printable aluminum alloy sets strength records, may enable lighter aircraft partsIncorporating machine learning, MIT engineers developed a way to 3D print alloys that are much stronger than conventionally manufactured versions.
- Study sheds light on musicians’ enhanced attentionBrain imaging suggests people with musical training may be better than others at filtering out distracting sounds.
Load more...
Loading...