 New nanoparticles stimulate the immune system to attack ovarian tumorsTargeted particles carrying the cytokine IL-12 can jump-start T cells, allowing them to clear tumors while avoiding side effects.
New nanoparticles stimulate the immune system to attack ovarian tumorsTargeted particles carrying the cytokine IL-12 can jump-start T cells, allowing them to clear tumors while avoiding side effects.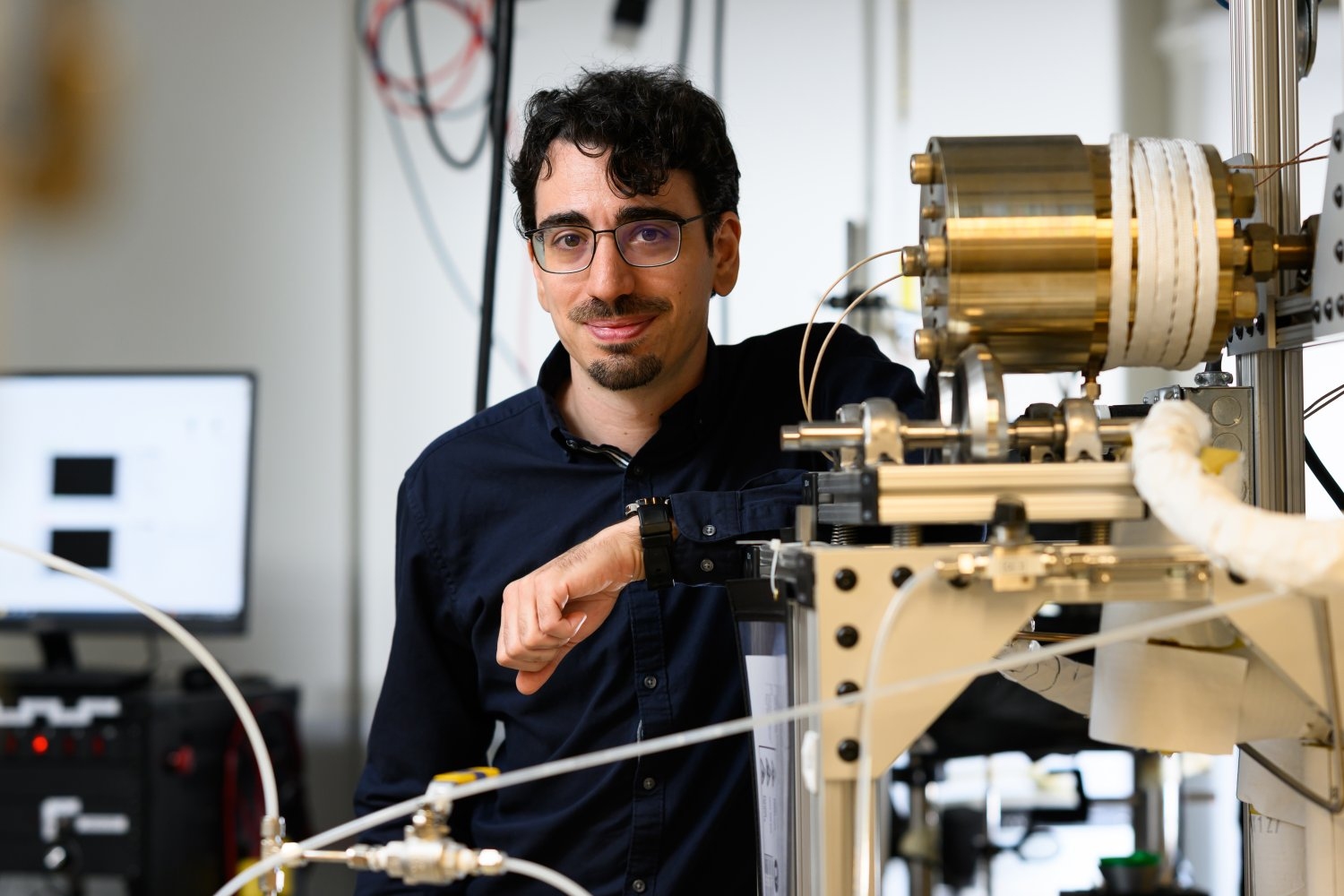 Using classic physical phenomena to solve new problemsMarco Graffiedi, a doctoral student in nuclear science and engineering, is researching quenching processes to help cool nuclear cores, and NASA craft the next generation of space vehicles.
Using classic physical phenomena to solve new problemsMarco Graffiedi, a doctoral student in nuclear science and engineering, is researching quenching processes to help cool nuclear cores, and NASA craft the next generation of space vehicles.
- Study reveals the role of geography in the opioid crisisThe findings point to state policies involving the presence of “pill mills” as influences on addiction over time.

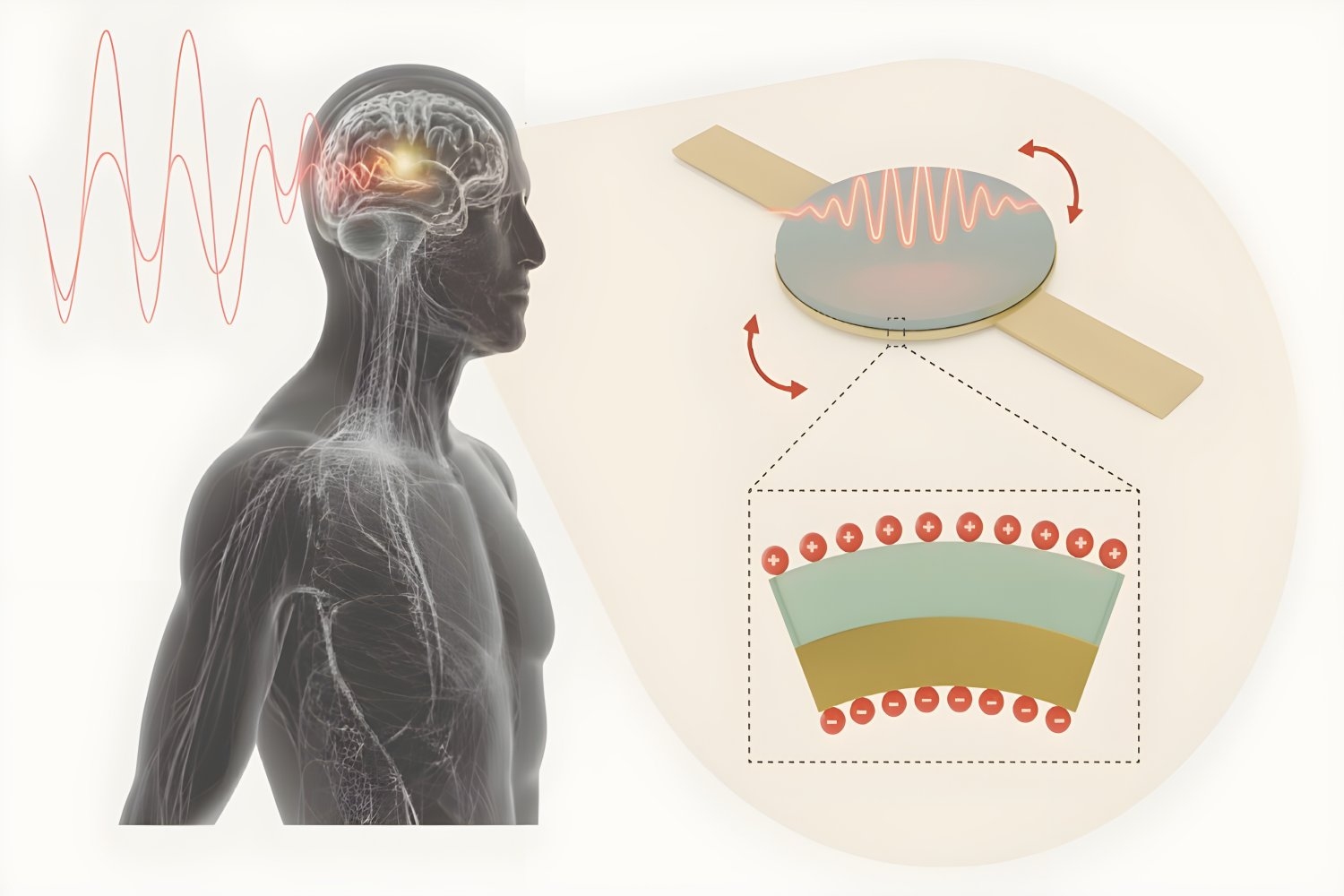
- Injectable antenna could safely power deep-tissue medical implantsThe technology would allow battery-free, minimally invasive, scalable bioelectronic implants such as pacemakers, neuromodulators, and body process monitors.
- Burning things to make thingsSili Deng, the Doherty Chair in Ocean Utilization and associate professor of mechanical engineering at MIT, is driving research into sustainable and efficient combustion technologies.

- Study: Identifying kids who need help learning to read isn’t as easy as A, B, CWhile most states mandate screenings to guide early interventions for children struggling with reading, many teachers feel underprepared to administer and interpret them.

- This is your brain without sleepNew research shows attention lapses due to sleep deprivation coincide with a flushing of fluid from the brain — a process that normally occurs during sleep.

- New method could improve manufacturing of gene-therapy drugsSelective crystallization can greatly improve the purity, selectivity, and active yield of viral vector-based gene therapy drugs, MIT study finds.
- Designing better, longer-lasting medicinesAdding amino acids to certain protein-based medications can improve stability and effectiveness. New MIT research demonstrates how it works.

- Astronomical data collection of Taurus Molecular Cloud-1 reveals over 100 different moleculesThe discovery will help researchers understand how chemicals form and change before stars and planets are born.
- The brain power behind sustainable AIPhD student Miranda Schwacke explores how computing inspired by the human brain can fuel energy-efficient artificial intelligence.

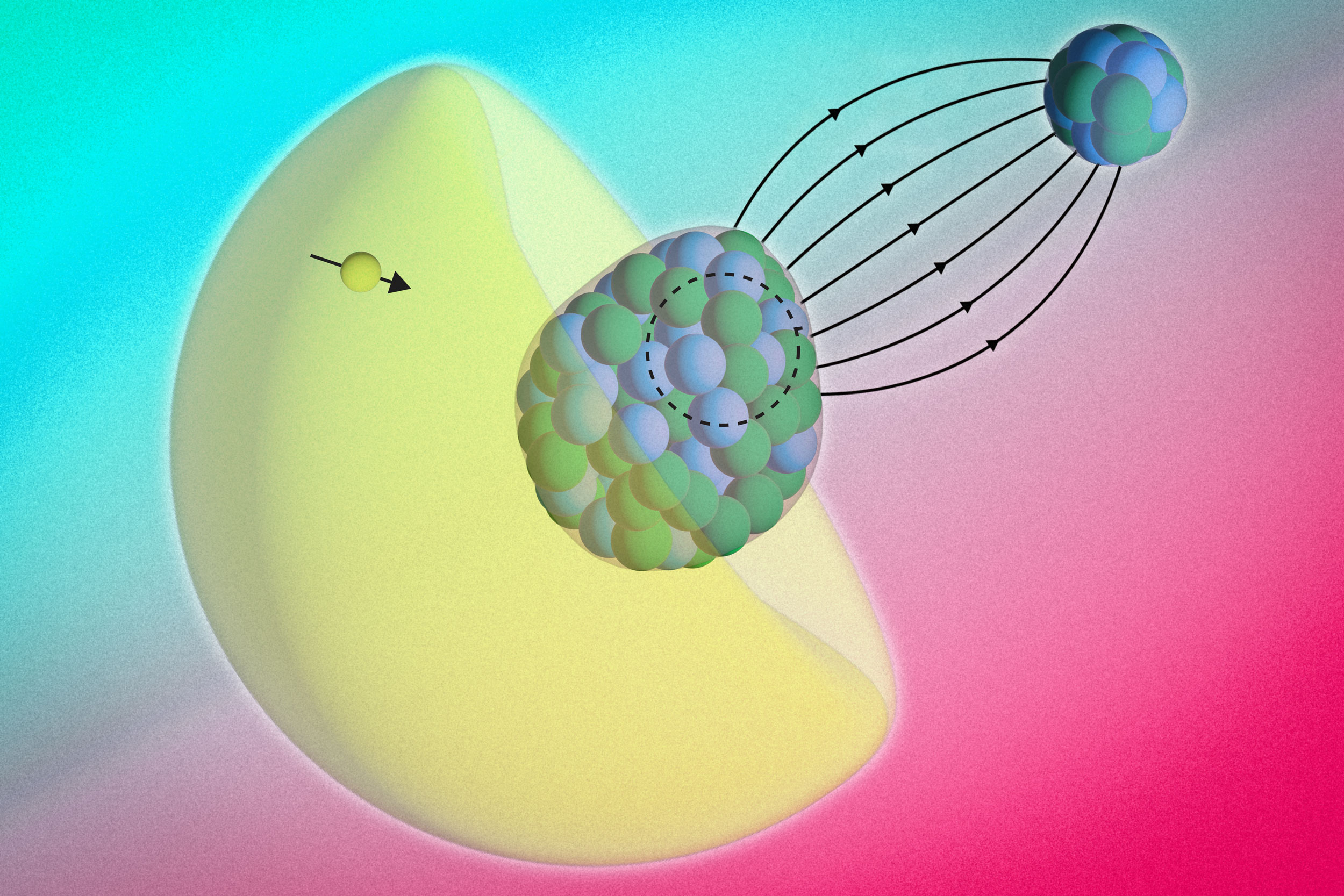
- With a new molecule-based method, physicists peer inside an atom’s nucleusAn alternative to massive particle colliders, the approach could reveal insights into the universe’s starting ingredients.
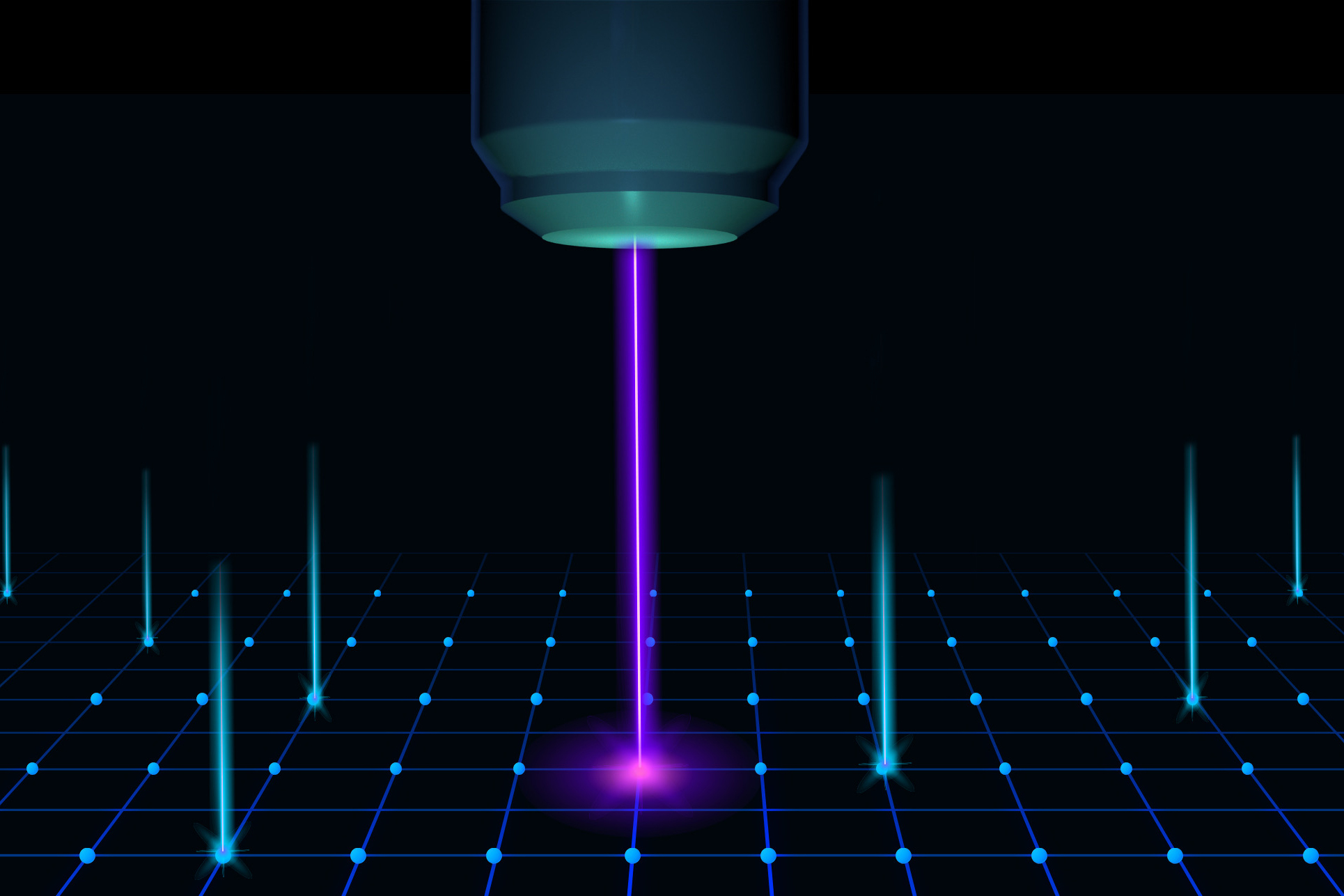
- A “seating chart” for atoms helps locate their positions in materialsThe DIGIT imaging tool could enable the design of quantum devices and shed light on atomic-scale processes in cells and tissues.
- Charts can be social artifacts that communicate more than just dataResearchers find that design elements of data visualizations influence viewers’ assumptions about the source of the information and its trustworthiness.

- Neural activity helps circuit connections mature into optimal signal transmittersScientists identified how circuit connections in fruit flies tune to the right size and degree of signal transmission capability. Understanding this could lead to a way to tweak abnormal signal transmission in certain disorders.
- Creating AI that mattersHow the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab is shaping AI-sociotechnical systems for the future.

- MIT Global Seed Funds catalyze research in over 20 countriesLaunched in 2008, the program has expanded exponentially and spent $30 million on high-impact research.

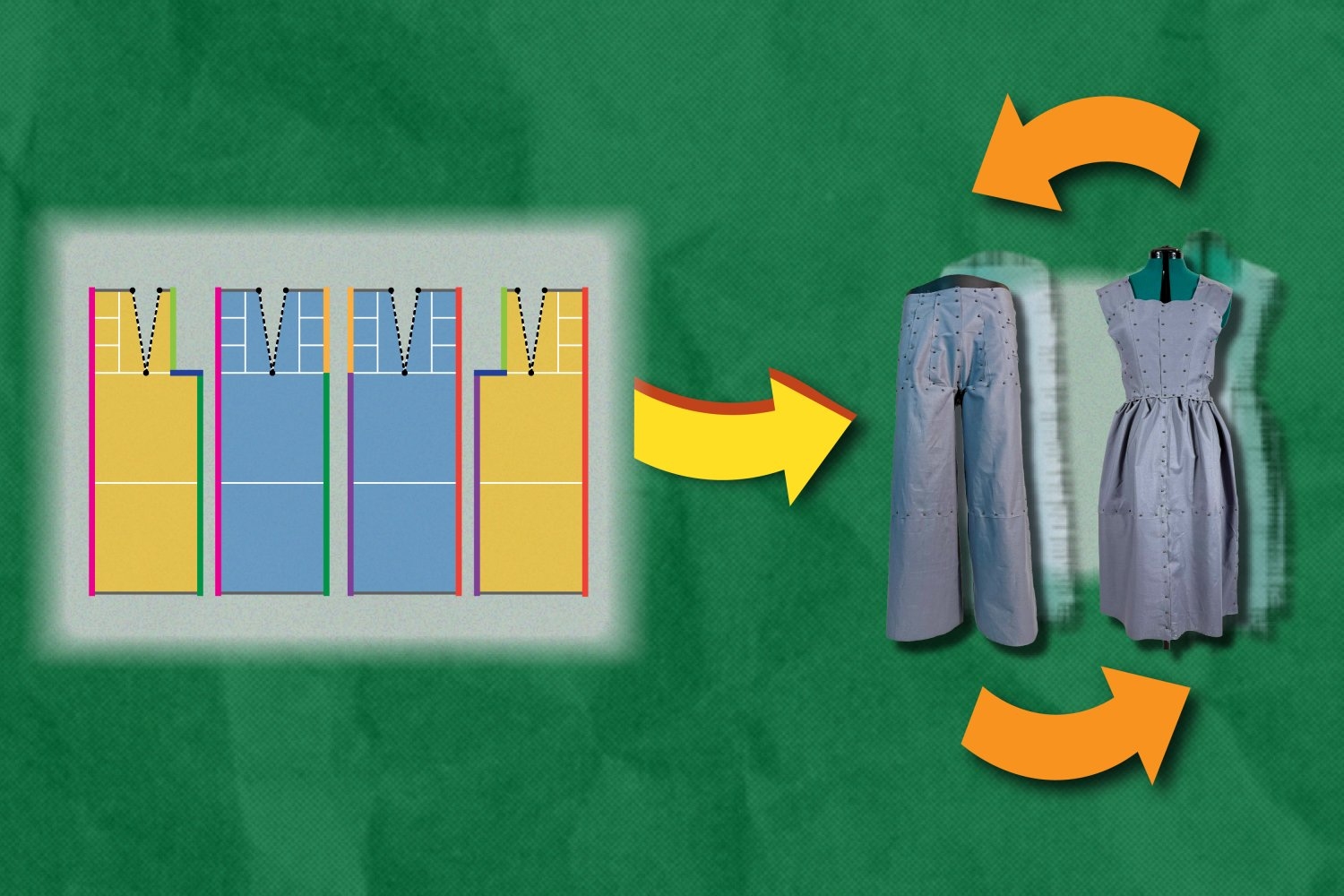
- New software designs eco-friendly clothing that can reassemble into new itemsTo reduce waste, the Refashion program helps users create outlines for adaptable clothing, such as pants that can be reconfigured into a dress. Each component of these pieces can be replaced, rearranged, or restyled.
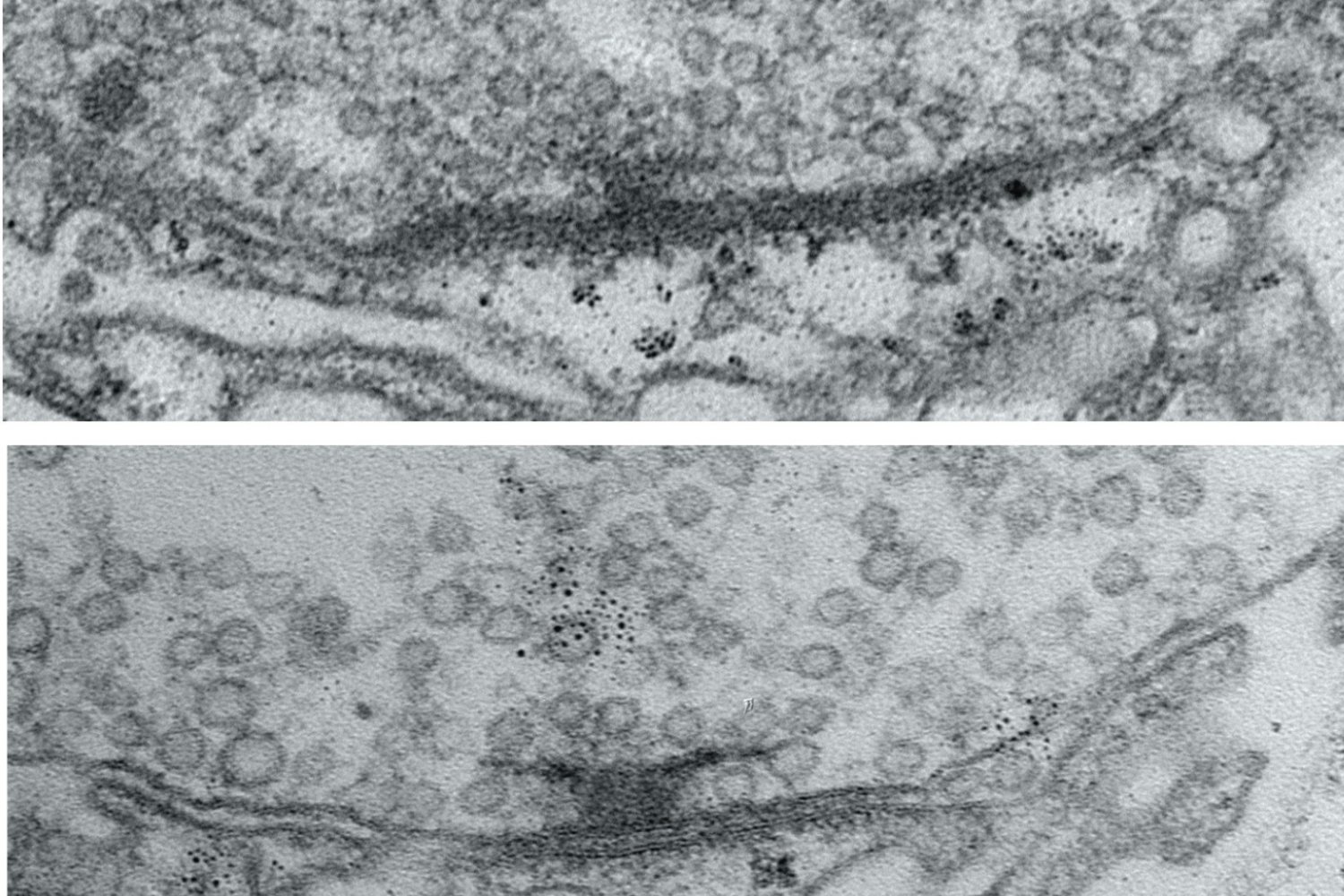
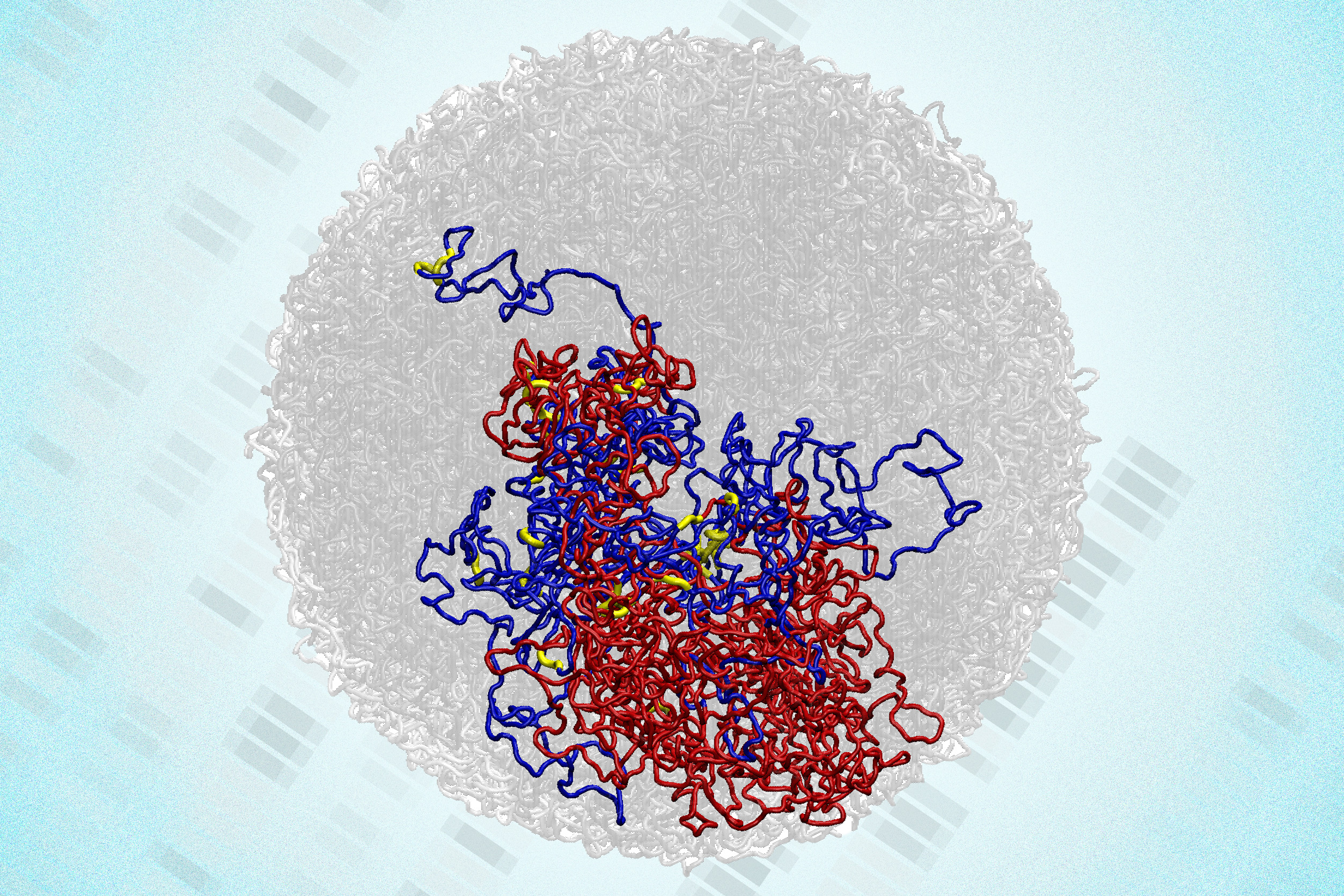
- In a surprising discovery, scientists find tiny loops in the genomes of dividing cellsEnabled by a new high-resolution mapping technique, the findings overturn a long-held belief that the genome loses its 3D structure when cells divide.
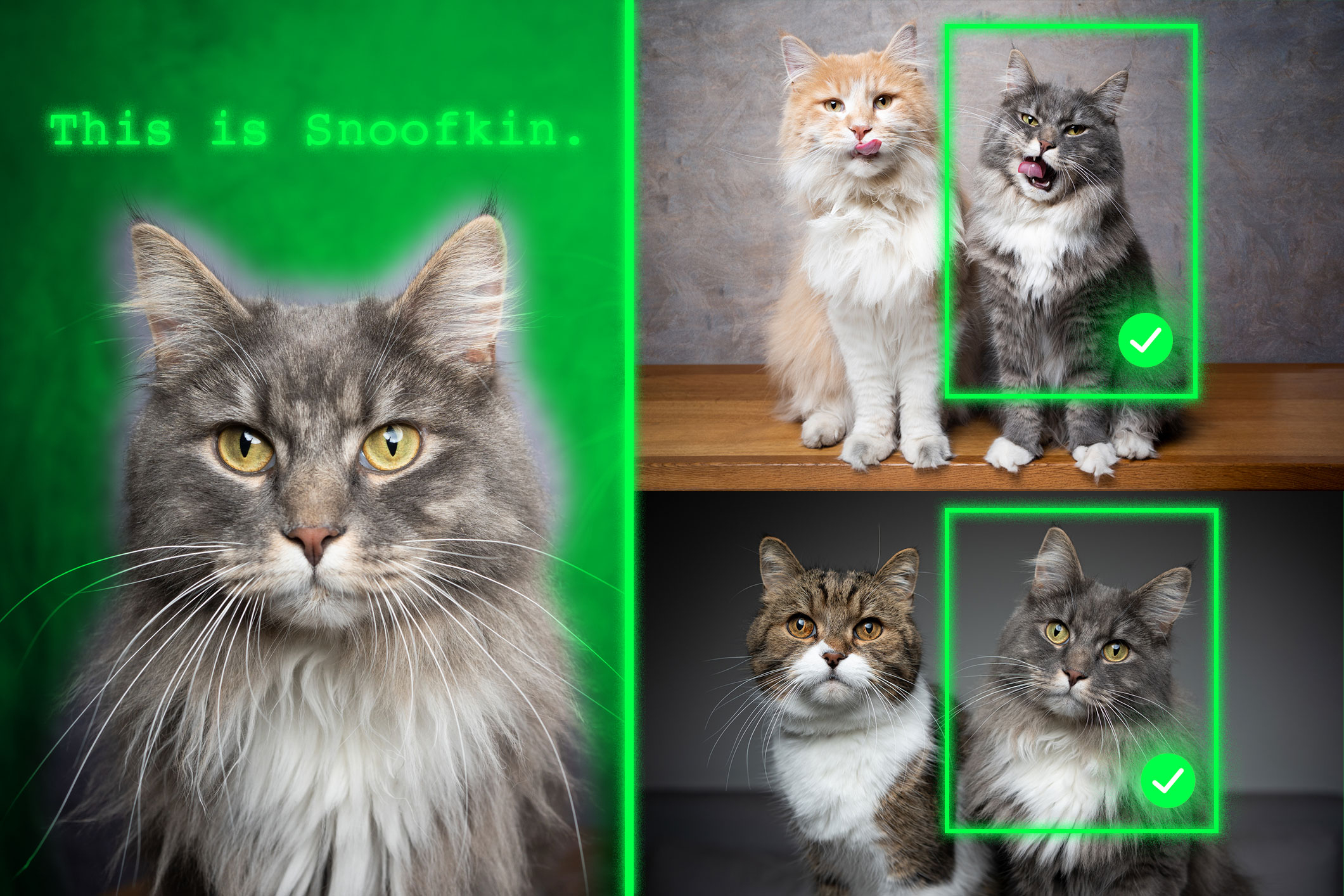
- Method teaches generative AI models to locate personalized objectsAfter being trained with this technique, vision-language models can better identify a unique item in a new scene.
- Darcy McRose and Mehtaab Sawhney ’20, PhD ’24 named 2025 Packard Fellows for Science and EngineeringMcRose, an environmental microbiologist, is recognized for researching the ecological roles of antibiotics in shaping ecosystems, agriculture, and health.

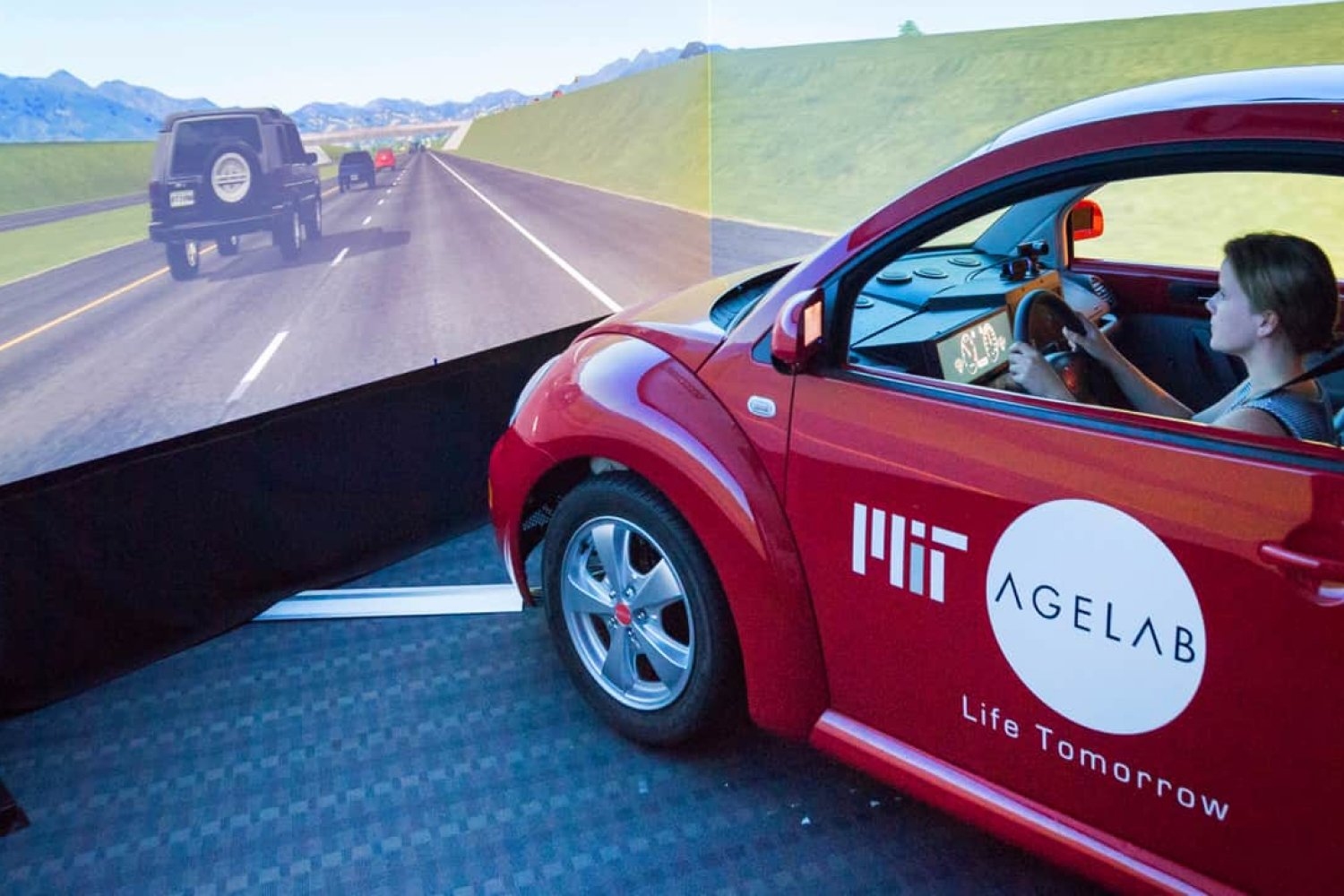
- MIT-Toyota collaboration powers driver assistance in millions of vehiclesA decade-plus alliance between MIT’s AgeLab and Toyota’s Collaborative Safety Research Center is recognized as a key contributor to advancements in automotive safety and human-machine interaction.

Load more...
Loading...